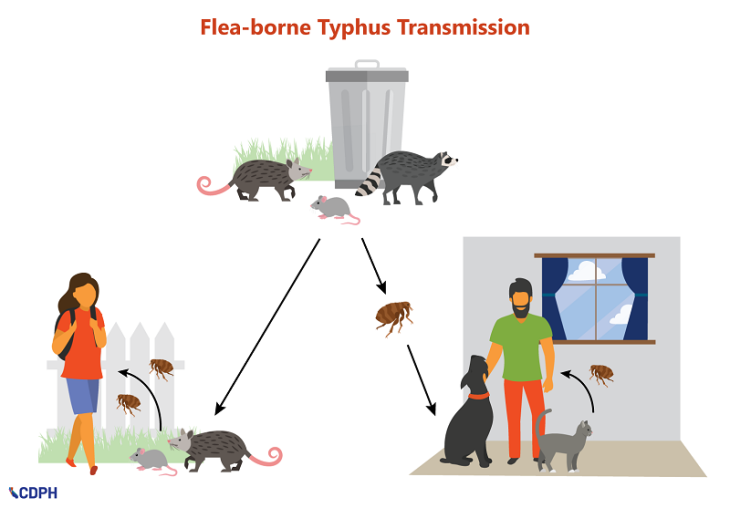
The NBA’s Rookie of the Year award often serves as both a blessing and a burden. Basketball analysts have noticed a concerning pattern where these celebrated newcomers frequently struggle to maintain their trajectory, with some even experiencing dramatic career declines after their inaugural success.
The Carter-Williams Paradox
Michael Carter-Williams stands as perhaps the most striking example of this phenomenon. The 2014 ROY winner dazzled the league with impressive numbers for the Philadelphia 76ers, but his career trajectory took a sharp downturn. By his third season, teams had thoroughly decoded his playing style, exposing limitations that weren’t apparent during his rookie campaign. ROY Betting becomes more popular season by season, be it basketball or baseball, since it is hard to predict the winner, but still a lot of fun.
Understanding the Decline
Several factors appear to contribute to this sophomore struggle:
1. Advanced Scouting: Teams accumulate detailed data on playing patterns
2. Adjusted Defensive Schemes: Opponents develop specific containment strategies
3. Increased Expectations: Mental pressure affects performance
4. Role Changes: Teams often modify how they utilize these players
The Evans Effect
Tyreke Evans represents another cautionary tale. His rookie numbers suggested future superstardom, but he never matched that initial success. Basketball experts point to several factors, including defensive adaptations by opponents and changes in team dynamics.
The Brogdon Exception
Malcolm Brogdon’s career path offers an interesting counterpoint. After winning ROY in 2017, he managed to improve gradually rather than decline. Some analysts attribute this to his mature age as a rookie and well-rounded skill set.
The Modern Context
Scottie Barnes’s recent experience with the Toronto Raptors provides a contemporary example. After winning ROY, Barnes has faced challenges maintaining his impact, despite showing flashes of brilliance. This situation highlights how even well-prepared young players can struggle with the adjustment.
Psychological Factors
Sports psychologists highlight several mental challenges these young players face:
– Increased media scrutiny
– Higher teammate expectations
– Personal pressure to improve
– Loss of the “underdog” mindset
Team Context Matters
Research indicates that ROY winners on losing teams often post inflated statistics that prove difficult to maintain. This “empty stats” phenomenon can create unrealistic expectations for future performance.
The Development Curve
Basketball development experts suggest that natural progression isn’t always linear. Some players need time to adjust after opponents adapt to their game, potentially leading to temporary performance dips.
League Evolution
The modern NBA’s pace and style may affect how rookies adapt. With increasing emphasis on three-point shooting and versatility, players face different challenges than previous generations.
International Impact
International players who win ROY often show different adaptation patterns, possibly due to their professional experience before entering the NBA. This factor deserves consideration when analyzing the sophomore slump phenomenon.
Prevention Strategies
Progressive teams employ various methods to combat the sophomore slump:
– Modified training programs
– Mental health support
– Gradual role expansion
– Managed expectations
Understanding past examples helps teams better prepare their young stars for long-term success. The key appears to lie in balanced development rather than immediate maximum exploitation of talent.
Statistical Context
While individual statistics often decline, some players show improvement in less obvious areas during their second season. This suggests the need for more nuanced evaluation methods.
The sophomore slump among ROY winners represents a complex challenge without simple solutions. As the NBA continues evolving, teams and players must adapt their approaches to development and expectations management.
Understanding these patterns helps teams and fans maintain realistic expectations while supporting young players through their crucial early development stages. The key lies not in avoiding the sophomore slump entirely, but in managing its impact and using it as a development tool.