BY MATTHEW BAJKO | Not all of California’s LGBT residents are benefiting from the state’s booming economy, according to a new report and an online data interactive component.
While LGBT people in California appear to be doing better than LGBT people nationwide, some regions of the state report the same levels of socioeconomic vulnerability as in the Southern and Midwestern states, according to the study by the Williams Institute at UCLA School of Law.
The study, titled “The LGBT Divide in California,” created by the LGBT think tank policy analyst Angeliki Kastanis, uses data from the 2010 U.S. Census and the 2012-2014 Gallup Daily Tracking Survey.
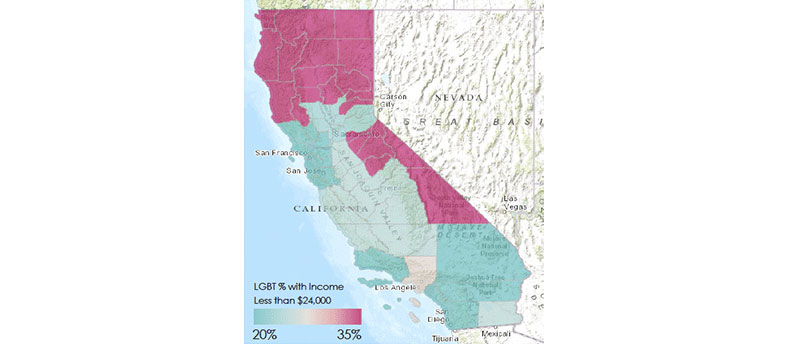
The report on the Golden State’s LGBT population was released last Thursday, January 21. Its findings are based on an estimated 1,334,000 LGBT residents in the state, 22 percent of whom live in the Bay Area.
Los Angeles County, with 31 percent, has the most LGBT residents, with the rest of southern California in second with 26 percent. The remaining residents reside in the Southern/Central Farm region, which includes an area along the border with Mexico east of San Diego County (10 percent), the Central Valley around Sacramento (6 percent), and the North and Mountain regions (4 percent).
“Using support for same-sex marriage as a proxy for measuring LGBT acceptance in the state, we see that the social climate varies by region,” noted Kastanis, who based the analysis on data from the Public Policy Institute of California. “The Central/Southern Farm region reports the lowest level of acceptance (40 percent), while the Bay Area reports the highest (67 percent).”
Among the findings is that LGBT people who live in the state’s Southern/Central farm region, encompassing the counties of Fresno, Imperial, Kern, Kings, Madera, Merced, Monterey, San Benito, San Joaquin, San Luis Obispo, Stanislaus, and Tulare, have a lower college completion rate than in the Southern and Midwestern regions of the United States.
Another eyebrow-raising finding in the report is that in the North and Mountain regions of California, the proportion of LGBT people earning less than $24,000 per year is similar to the rate in the Southern and Midwestern regions of the United States.
“Identifying the most vulnerable sub-groups within the LGBT community in California could help pinpoint where supportive programs and policies are needed most,” stated Kastanis, who was the institute’s 2015 Peter J. Cooper Fellow and received a Master of Public Policy from the Irving B. Harris School of Public Policy at the University of Chicago.
Several of her findings mirror previous reports that have documented disparities between Caucasian and people of color LGBT residents as well as men and women in the LGBT community.
Kastanis found that lesbian, bisexual, and transgender women in California are more likely to report an annual income of less than $24,000 (30 percent) than gay, bisexual, and transgender men (23 percent).
“Even so, LGBT females in California are doing slightly better than the national LGBT estimates for each indicator of socioeconomic well-being,” according to the study’s accompanying online data interactive.
The state’s LGBT Latino/as are twice as likely as white LGBT Californians to report earning less than $24,000 annually, according to the report, while African American LGBTs in California are 1.5 times as likely.
Kastanis’ report also noted that even in urban centers where LGBT support is high, such as Los Angeles County, there are pockets of LGBT residents that face greater socioeconomic disparities.
Yet compared to their counterparts in other states, LGBT Californians “as a whole,” concluded Kastanis, are doing better on such indicators as educational attainment, income, and money for health care.
The report breaks down the United States into five zones, with the Northeast – at 29 percent – having the least amount of LGBT people making less than $24,000. The Pacific region was second at 30 percent, while the Mountain and South zones each were at 33 percent. In last place was the Midwest at 35 percent.
“According to our U.S. regional data interactive, the LGBT Divide, the Pacific states are generally doing well when looking at measures of well-being,” states the report. “Data for the Pacific states are mainly driven by California’s numbers, as California accounts for 77 percent of all LGBT adults living in the Pacific states.”